Chris Newton
GIS & Data Analytics
Agent-Based Modelling
Agent based models (ABM) have been increasingly applied in computational social sciences since the 1970s (Conte and Paolucci, 2014). They are often used to observe emerging behavioural patterns and have been applied to research ranging from testing policy impacts, traffic modelling, the spread of disease, and economic behaviours (Conte & Paolucci, 2014).
ABM lends itself well to analysing decision making behaviour in a range of modelled contexts. Previous ABM research has examined dietary behaviours (Conte & Paolucci, 2014), cognitive inconsistencies (Evans et al., 2016) and behaviour change intervention strategies (Mercuur, 2015), so ABM may be highly relevant to my research project.
For this initial project, a simple ABM was created in which agents move around an environment randomly:
def move(self):
if random.random() < 0.5:
self.x = (self.x + 1) % 300
else:
self.x = (self.x - 1) % 300
…collecting a hypothetical resource from the environment:
def eat(self):
if self.environment[self.y][self.x] > 10: #if the environment value is greater than 10...
self.environment[self.y][self.x] -= 10 #remove 10 from the environment...
self.store += 10 #...and store it in the agent.
#eat what is left-
elif self.environment[self.y][self.x] < 10: #if the env value is less than 10...
self.store += self.environment[self.y][self.x] #...the agent eats it...
self.environment[self.y][self.x] = 0 #..so zero remains.
…and sharing the resource with any other agents they encounter on their travels:
def share_with_neighbours(self, neighbourhood):
#Loop through the agents in self.agent
random.shuffle(self.agent) #randomise the order to avoid earlier ones having an unfair advantage.
for agent in self.agent:
dist = self.distance_between(agent) # Calculate the distance between self and the current other agent
if dist <= neighbourhood: # If distance is less than or equal to the neighbourhood
sum = self.store + agent.store #take the sum of the agents' stores and divide them equally
ave = sum / 2
self.store = ave
agent.store = ave
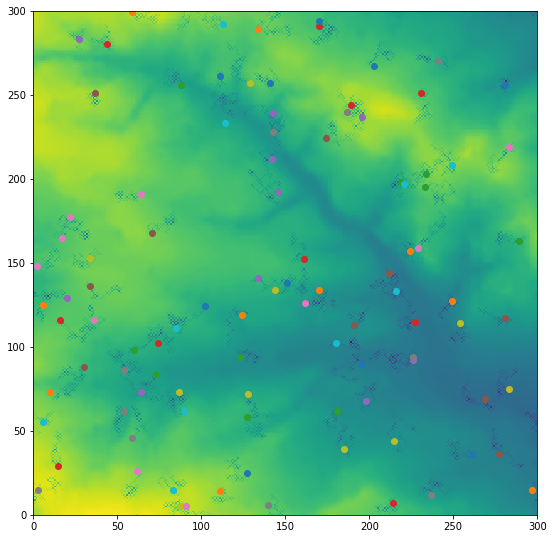
The GitHub repository for the project can be found here.
References
Conte, R. and Paolucci, M., (2014). On agent-based modeling and computational social science, Frontiers in Psychology, 5, pp.1-9.
Evans, O., Stuhlmüller, A. and Goodman, N.D., (2016). Learning the Preferences of Ignorant, Inconsistent Agents, Proceedings of the 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, Arizona, USA. 12th-17th February 2016, pp. 323-329.
Mercuur, R.A., (2015). Interventions on Contextualized Decision Making: an Agent-Based Simulation Study (Master’s thesis: available from https://dspace.library.uu.nl/handle/1874/323482).